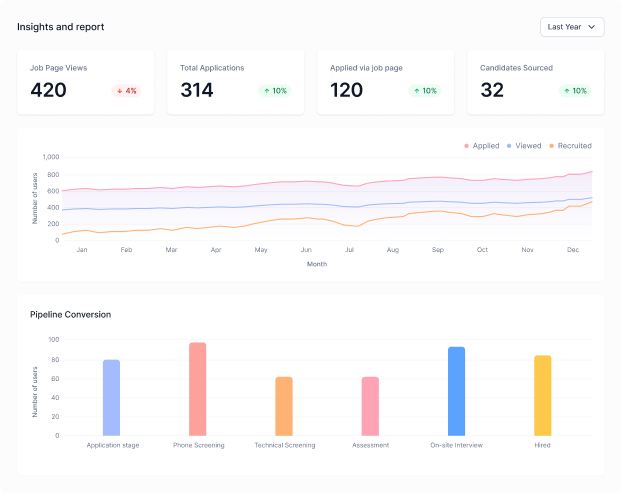
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping industries across the globe, and Africa is no exception. As the world’s youngest continent, with a rapidly growing population and an expanding digital economy, Africa holds immense potential to harness AI for transformative growth. However, alongside the opportunities come unique challenges that must be addressed to ensure equitable and sustainable integration of AI technologies.
In this post, we will explore how AI is transforming industries in Africa, the opportunities it presents, and the hurdles that need to be overcome for AI to reach its full potential on the continent.
AI’s Transformative Impact on African Industries
1. Healthcare
Access to quality healthcare has long been a challenge in many African countries. AI is emerging as a game-changer by addressing gaps in diagnostics, treatment, and healthcare delivery.
- Diagnostics: AI-powered tools like image recognition algorithms are being used to detect diseases such as malaria and tuberculosis with remarkable accuracy. Startups like 4D Healthware and Zipline are leveraging AI to improve diagnostics and medical supply delivery in remote areas.
- Telemedicine: AI-driven chatbots and telemedicine platforms are helping patients in underserved regions connect with healthcare professionals, reducing the strain on overburdened healthcare systems.
2. Agriculture
Agriculture employs over 60% of Africa’s workforce, making it a critical sector for economic development. AI is playing a pivotal role in increasing agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Crop Monitoring: AI-powered drones and satellite imagery are helping farmers monitor crop health and optimize irrigation and fertilization. Companies like Hello Tractor are using AI to connect farmers with tractor services, improving efficiency.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models analyze weather patterns to provide farmers with precise forecasts, helping them mitigate risks associated with climate change.
3. Financial Services
AI is driving financial inclusion by making banking and credit services accessible to millions of unbanked Africans.
- Credit Scoring: Traditional credit systems often exclude individuals without formal employment. AI-based systems analyze alternative data, such as mobile phone usage and social media activity, to provide credit scores, enabling access to microloans.
- Fraud Detection: AI-powered systems are enhancing security in digital transactions, a critical need as mobile money platforms like Paga continue to grow.
4. Education
Africa’s education systems are strained by large student populations and limited resources. AI offers scalable solutions to bridge the gap.
- Personalized Learning: AI-driven platforms like Ubongo and uLesson provide personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs.
- Teacher Training: AI tools can upskill teachers by offering training modules and real-time feedback, improving the quality of education delivery.
Opportunities Presented by AI in Africa
1. Job Creation
Contrary to fears of automation leading to job losses, AI can create new roles in data labeling, software development, and AI model training. Initiatives like Samasource have already created thousands of jobs by outsourcing AI training data tasks to African workers.
2. Innovation Ecosystems
AI is fueling the growth of innovation hubs across Africa, from Nairobi’s Silicon Savannah to Lagos’ Yabacon Valley. These ecosystems are attracting investments and fostering the development of local AI-driven solutions.
3. Solving Local Challenges
One of the most promising aspects of AI in Africa is its ability to address uniquely African challenges. For instance, AI models trained on local dialects are bridging language barriers in communication and education.
4. Global Competitiveness
AI adoption can position African businesses to compete globally by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and fostering innovation. For example, AI-powered chatbots and customer service tools are enabling African tech platforms to provide world-class service.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Africa
1. Limited Infrastructure
AI technologies require robust digital infrastructure, including high-speed internet and data centers. While internet penetration is growing, significant disparities remain between urban and rural areas.
2. Data Availability and Bias
AI systems thrive on large datasets, but Africa faces challenges in data collection and management. Moreover, AI models trained on data from other regions may not perform effectively in African contexts, leading to biases and inaccuracies.
3. Skills Gap
The lack of AI expertise is a major hurdle. While initiatives like AI Saturdays and partnerships with organizations such as DeepMind are helping to build capacity, the demand for skilled AI professionals far exceeds the supply.
4. Regulatory and Ethical Concerns
The rapid adoption of AI raises questions about data privacy, security, and ethical use. Many African countries lack comprehensive policies to govern AI deployment, leaving room for misuse.
5. Cost of Adoption
Developing and implementing AI solutions can be expensive, making it challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to adopt these technologies.
What Needs to Be Done?
To unlock the full potential of AI in Africa, concerted efforts are needed from governments, private sectors, and international organizations:
1. Invest in Infrastructure
Governments and private investors must prioritize the development of digital infrastructure, including reliable internet access and cloud computing facilities.
2. Foster Local AI Talent
Educational institutions and tech hubs should collaborate to provide specialized training in AI and related fields. Scholarships and mentorship programs can encourage more students to pursue careers in AI.
3. Promote Data Sovereignty
African countries should invest in local data collection and storage systems to ensure that AI models are trained on relevant and unbiased datasets.
4. Create Inclusive Policies
Governments need to establish regulations that promote ethical AI use, protect data privacy, and ensure equitable access to AI technologies.
5. Encourage Public-Private Partnerships
Partnerships between governments, tech companies, and NGOs can accelerate AI adoption by pooling resources and expertise.
Conclusion
The rise of AI in Africa is a double-edged sword, offering unparalleled opportunities while posing significant challenges. By leveraging its youthful population, entrepreneurial spirit, and growing tech ecosystems, Africa can harness AI to drive socioeconomic development. However, success will depend on addressing infrastructure gaps, building local capacity, and enacting policies that promote equitable and ethical AI use.
As the continent continues its journey into the AI era, it has the chance to not only benefit from this transformative technology but also to shape its global future. The time to act is now.