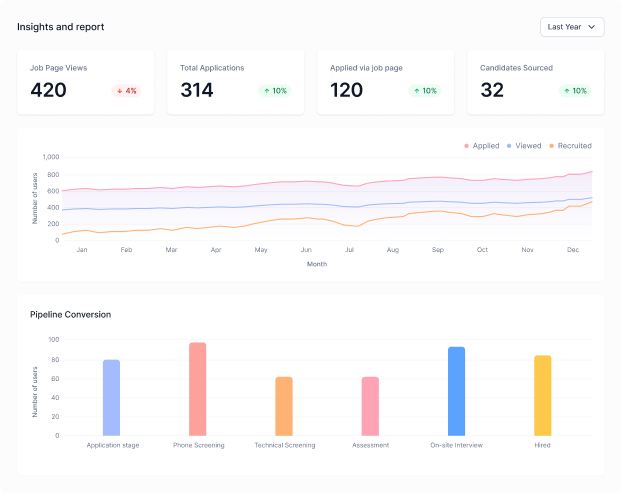
Recruiting talent is a critical aspect of any business, serving as the foundation upon which organizations build their success. Finding the right person for the right role can significantly impact an organization’s overall productivity and growth.
In recent years, advancements in technology have introduced tools like AI to streamline and enhance the recruitment process, leading many to question the role of human recruiters. While AI is becoming an essential part of the hiring toolkit, human recruiters bring irreplaceable value. This article explores when to use AI, when human recruiters should take the lead, and why combining both approaches can lead to the best outcomes.
What is AI in Recruitment?
AI in recruitment refers to the use of machine learning, algorithms, and data-driven tools to perform tasks traditionally handled by human recruiters. These tasks include resume screening, initial interviews, and even performance prediction.
AI can process massive amounts of data in a fraction of the time it would take a human recruiter. It helps companies identify the best candidates by analyzing resumes, assessing qualifications, and using predictive analytics to forecast job performance.
For instance, AI can screen resumes to match specific keywords, highlighting candidates who meet the job requirements. It can also analyze patterns from previous successful hires and recommend candidates who are likely to succeed in similar roles. AI’s ability to learn and adapt makes it a powerful tool in recruitment.
However, AI is not meant to replace human recruiters. Instead, it’s a tool to support them, handling time-consuming, repetitive tasks so human recruiters can focus on more strategic aspects of the hiring process.
Benefits of AI in Recruitment
Speed and Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of AI in recruitment is the speed with which it can process applications. In a world where job openings can attract hundreds or thousands of applications, human recruiters often struggle to sift through them all in a timely manner. AI tools can scan and rank candidates based on predefined criteria within minutes, dramatically reducing the time spent on initial screenings.
Moreover, AI tools can automate repetitive tasks such as sending emails, scheduling interviews, and following up with candidates. By automating these tasks, AI frees up recruiters to focus on higher-value activities, like relationship-building and strategy.
Reduced Bias
Bias is a significant issue in recruitment. Human biases, whether conscious or unconscious, can influence hiring decisions, sometimes leading to discrimination based on factors like gender, age, race, or background. AI can help mitigate this issue by making decisions based on data rather than personal feelings or prejudices.
AI tools can be programmed to ignore irrelevant factors like names, photos, or demographic information and focus solely on the qualifications and experience that matter for the role. This leads to a more objective and fair hiring process, which is crucial for promoting diversity and inclusion within an organization.
AI Interviewers
AI-powered systems can conduct initial interviews, analyzing candidates’ responses, body language, and even tone of voice to assess their suitability for the role. AI interviewers provide consistent evaluations across all candidates, ensuring a standardized and fair process.
For instance, an AI interviewer can assess how well a candidate communicates, their problem-solving abilities, and their confidence during an interview. These insights can then be used to rank candidates and identify those who may be a good fit for the role. While AI interviewers are not yet capable of replacing human interviews entirely, they provide valuable support in the early stages of the hiring process.
Companies hiring at a global scale are increasingly using AI interviewers, such as Loubby AI’s Interview Co-Pilot. These AI systems can conduct basic interviews by asking candidates pre-set questions and analyzing their answers. AI interviewers are helpful for initial screening, but human recruiters usually step in for deeper interviews later in the process.
For companies hiring for many positions simultaneously, AI can take the lead in the early stages by quickly screening candidates. Once AI has narrowed down the list, human recruiters can step in to assess the candidates more deeply, looking at cultural fit and other factors that require a personal touch.
Predictive Analytics
AI recruitment tools excel in predictive analytics, which helps forecast which candidates are likely to be successful in a given role. By analyzing data from past hires and matching it with the current candidate pool, AI can predict future job performance. For example, if a company has data on what makes a successful salesperson (e.g., specific skills, experience, or personality traits), AI can identify candidates who share these characteristics and recommend them for the role.
Predictive analytics can also help with workforce planning, identifying potential gaps in skills and suggesting recruitment strategies to address these needs. This is particularly valuable in large organizations or industries where specific skills are in high demand.
The Value of Human Recruiters
While AI offers numerous benefits, human recruiters are irreplaceable when it comes to certain aspects of the hiring process. Recruitment is not just about finding the right skills or qualifications; it’s about understanding a candidate’s motivations, assessing cultural fit, and building relationships that can turn a job offer into a long-term partnership. Here’s why human recruiters are still essential:
Emotional Intelligence and Empathy
One of the greatest strengths human recruiters bring to the table is emotional intelligence. Recruitment is, at its core, about people. Understanding the emotions, motivations, and aspirations of candidates is crucial in determining whether they are the right fit for both the job and the company.
Human recruiters can assess a candidate’s personality, evaluate their responses in nuanced ways, and connect with them on a personal level. This emotional connection is vital in creating a positive candidate experience, especially for high-stakes roles or senior positions where cultural fit and personal motivations are key.
Handling Complex Negotiations
AI may be great at handling data-driven tasks, but when it comes to complex negotiations like salary expectations, benefits packages, or managing counteroffers, human recruiters excel. Negotiating is a delicate process that often requires emotional intelligence, persuasion, and flexibility. Human recruiters can gauge how a candidate feels about an offer, understand their priorities, and adjust the negotiation strategy accordingly.
For example, a candidate might value flexible working hours or the option to work remotely. A human recruiter, through discussions with the candidate, can modify the offer to provide flexibility, facilitating a personalized work-life balance that meets the candidate’s needs.
In contrast, AI may have difficulty recognizing these preferences due to its lack of interpersonal insight, which could result in missing the chance to customize the offer in a manner that accommodates both the candidate and the company’s guidelines.
Assessing Cultural Fit
Cultural fit is a critical factor in hiring decisions, particularly for roles that require strong teamwork or leadership skills. Human recruiters are skilled at evaluating whether a candidate’s values, personality, and work style align with the company’s culture. They can ask open-ended questions and interpret responses in ways that AI cannot.
For example, in a final interview, a human recruiter can ask a candidate about their previous experiences in different work environments, how they handle conflict, or how they approach team collaboration. The recruiter can then assess whether the candidate’s approach aligns with the company’s culture and values.
Building Relationships with Candidates
Building strong relationships with candidates is one of the key roles of a human recruiter. These relationships can make or break a candidate’s decision to join a company. A human recruiter can provide personalized feedback, answer questions in real-time, and make candidates feel valued throughout the process. This personal touch helps candidates feel more comfortable and engaged, leading to better hiring outcomes.
Moreover, candidates who have a positive experience with a recruiter are more likely to accept an offer and stay with the company long-term. Human recruiters are adept at fostering this relationship, which is essential in today’s competitive job market.
AI and Human Recruiters: A Perfect Partnership
Rather than viewing AI and human recruiters as opposing forces, it’s best to see them as complementary tools. Each has its strengths, and when used together, they can create a more efficient, fair, and effective recruitment process.
When to Use AI
- Initial Screening: AI excels at sifting through large volumes of resumes and identifying candidates who meet the basic qualifications for a role. This allows human recruiters to focus on more in-depth assessments later in the process.
- Data Analysis: AI tools can analyze past hiring data, industry trends, and performance metrics to predict which candidates are most likely to succeed in a given role.
- Automating Repetitive Tasks: Scheduling interviews, sending follow-up emails, and handling initial correspondence can all be automated by AI, saving recruiters valuable time.
When to Use Human Recruiters
- Final Interviews: Human recruiters are better suited for evaluating soft skills, emotional intelligence, and cultural fit. They can ask open-ended questions, interpret nuanced responses, and assess how well a candidate aligns with the company’s values.
- Building Relationships: Personal interactions are crucial when it comes to creating a positive candidate experience. Human recruiters can build rapport, address candidate concerns, and make the hiring process more engaging and personalized.
- Complex Roles: Leadership positions or roles with unique requirements often require a more tailored approach. Human recruiters can adapt their strategies to meet the specific needs of these positions, something that AI might struggle with.
Real-World Example: AI and Human Recruiters Working Together
Let’s take an example of a company looking to hire a software developer. The company receives 500 applications for the role. Instead of manually reviewing each one, they use an AI-powered Applicant Tracking System (ATS) to filter out unqualified candidates and rank the remaining ones based on skills, experience, and other criteria. This narrows the pool down to 50 candidates.
Next, an AI interviewer conducts virtual interviews with the top 50 candidates, assessing their communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and other relevant factors. After this step, the AI provides a list of the top 10 candidates who are most likely to succeed in the role.
At this point, human recruiters step in to conduct final interviews, assessing soft skills, cultural fit, and motivation. They also handle negotiations and manage the candidate experience. In the end, the company makes a data-driven, well-rounded decision, combining the efficiency of AI with the personal touch of human recruiters.
The Growing Importance of AI in Recruitment
The adoption of AI in recruitment is not just a passing trend—it’s becoming a necessity for staying competitive. According to Gartner, 76% of HR leaders believe that without adopting AI solutions like these, their organizations will fall behind in the next 12 to 24 months compared to those that do. This statistic emphasizes the growing importance of integrating AI into the recruitment process.
AI allows businesses to process more data, make faster decisions, and reduce bias, all while freeing up human recruiters to focus on relationship-building and strategic decision-making. Companies that embrace AI in recruitment are not only able to hire more efficiently but are also better positioned to attract and retain top talent in today’s competitive job market.
Conclusion
The future of recruitment lies in the partnership between AI and human recruiters. AI is a powerful tool for handling repetitive tasks, analyzing data, and making objective decisions based on predefined criteria. Meanwhile, human recruiters bring emotional intelligence, creativity, and adaptability to the table. When used together, AI and human recruiters can create a hiring process that is both efficient and human-centered.
As businesses continue to adapt to changing technologies, it’s clear that AI will play an increasingly important role in recruitment. However, human recruiters will always be essential for tasks that require emotional intelligence, cultural fit assessments, and complex negotiations. By combining the strengths of both, companies can build a recruitment strategy that ensures they hire the best talent, foster positive candidate experiences, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving job market.